Technical Support技术支持
CONTACT US
 400 179 0116
400 179 0116
24-hour service hotline marketing@ldraft.comE-mail
marketing@ldraft.comE-mail
Corneal cell separation
source:QiDa technoligy views:1499 time:2023-05-10
How to extract the corneal limbal mesenchymal matrix required for the experiment? Here are our extraction steps, with a focus on how to extract the primary material without getting lost:
Preparation of reagents:
12 hole plate, tip of micro pipette, 60mm cell culture dish, 100mm cell culture dish
Syringe filter 0.2 μ m. 10 # disposable scalpel blade, 15mL conical tube
The best choice for T75 culture bottle is Corning, reversible cell filter, cell filter 20 µ m, FACS tube (5 mL polystyrene round bottom tube, Falcon, catalog number 352058), collagenase A, Dulbecco phosphate buffer saline (Qida article number: SD0030)
0.25% trypsin EDTA, MSCM stem cell culture medium (low serum), FGM fibroblast culture medium, 70% ethanol, 0.5 M EDTA, CD90, CD44, mouse IgG2a, k isotype APC, cytokeratin AE1/AE3, 4 ', 6-diamino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)
Cell separation steps:
1. Place the limbal segment of the cornea in a 60 mm culture dish containing 5 mL collagenase a (2 mg/mL) and cut it with a surgical blade
Cut the corneal limbus into smaller parts (2-3 pieces). Cultivate at 37 ° C and 5% carbon dioxide, digest overnight with collagenase, and obtain corneal limbal cell clusters.
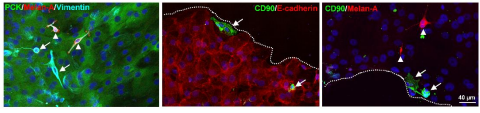
2. After culture, use 1mL pipette to blow up and down, blow the cell suspension in the culture dish, and observe the existence of cell clusters and single cells under the microscope. This cell cluster should be composed of corneal limbal epithelial cells, stromal cells and melanocytes (such as shown in Figure 1).
Note: If the corneal limbus is not fully digested after overnight cultivation and grinding, it should be cultured in the same solution at 37 ° C with 5% CO2 for another 2 hours to achieve complete digestion. On the contrary, excessive digestion of tissues (over 20 hours) may affect cell viability and cell quality.
A. Cut the corneal sclera margin (left) into a fan-shaped shape, and cut each fan-shaped edge area (right) 1mm before and after. From Polisetti et al. (2019) literature.
B. The corneal limbal clusters and single cell solutions formed by incubating different sizes of corneal limbal segments in collagenase overnight are different (magnified x40 times).
C. Filter edge clusters separated from individual cells.
D. Single cells require trypsin EDTA to digest corneal limbal clusters and form corneal limbal cell suspensions
3. Use a cell filter with a pore size of 20 µ m to separate corneal limbal cell clusters from individual cells. Cells that did not pass the cell filter and clusters to be retained were cleaned twice with DPBS to remove any remaining individual cells. Reverse the filter and place it on a 60mm plate. Add 0.25% trypsin EDTA (5 mL) to rinse the clusters into a culture dish and incubate at 37 ° C for 10-15 minutes to dissociate the clusters into individual cells.
Note: A 37 µ m reversible cell filter can be used instead of a 20 µ m cell filter. After centrifugation of a single cell suspension, corneal fibroblasts were obtained and directly cultured using FGM (Qida Biotech: P6001) (Figure 2), resulting in corneal fibroblasts.

Continue with corneal stromal cell extraction:
4. After incubation, use 1mL pipette to blow up and down to develop cell suspension. Until I see
Stop blowing the cell suspension under the microscope. Add 5 mL of preheated DMEM containing 10% FBS (37 ° C water bath) to inhibit trypsin digestion. Transfer the cell suspension to a 15mL centrifuge tube at a rate of 200 × Centrifuge for 5 minutes.
Note: If the cluster does not completely dissociate after 15 minutes of incubation and grinding, stir in collagenase at 37 ° C and 5% CO2 for another 5 minutes to achieve complete dissociation. On the contrary, prolonged digestion of clusters may have adverse effects on cell viability and cell quality.
5. After centrifugation, fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) was performed by adding 200 µ L FACS buffer (see Formula 3) through P200 pipette
Transfer the cell suspension to FACS tube (100 µ L/tube), and add anti human conjugated with mouse APC to connect CD90 antibody (5 µ L/106 cells) to one tube, and connect IgG2a isotype APC to another tube at 4 ° C. Gently vortex the sample and incubate it on ice for 45 minutes, tapping lightly every 15 minutes.
Note: If the number of cells is high, i.e. more than 10 ^ 6 cells, adjust the volume and concentration of the antibody according to the number of cells
After cultivation, add 1mL of FACS buffer to each FACS tube and adjust the cells to 400 × Centrifuge for 5 minutes and repeat washing twice.
After washing, add 500 µ L of FACS buffer containing DAPI (1:5000) to eliminate dead cells before continuing using FACS Aria II classifier for flow sorting (refer to Polisetti et al., 2022)
6. Culture of corneal limbal mesenchymal stromal cells
Seed the sorted CD90+LMSC onto the holes of the 12 well plate.
Note: The number of CD90+cells (150-900) per corneal margin varies depending on the sample. The CD90 population mainly contains LEPC, which can be enriched using cell type specific culture media (refer to Polisetti et al., 2020).
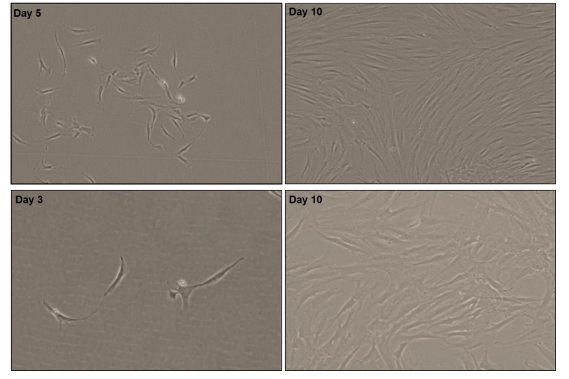
Cultivate LMSC in MSCM (Qida product number: P2001) (Figure 3) complete medium at 37 ° C and 5% CO2. Change the fluid every 2 days.

Observe the morphology of LMSC through a phase contrast microscope. LMSC is characterized by spindle shaped elongated cells with prominent nucleoli (Figure 4).
7. Passage of corneal limbal mesenchymal stromal cells
1.When the cell grows to a confluence of over 80-85%, it begins to prepare for passage;
2. Wash cells with DPBS and add 1mL of trypsin EDTA (0.25%; preheated in a water bath at 37 ° C).
Incubate at room temperature for 1-3 minutes.
3. After observing the cells under a microscope and becoming elliptical and translucent, gently tap the cell bottle wall, add 2mL of MSCM complete culture medium to inhibit the action of trypsin, and mix thoroughly.
4. Transfer the cell suspension to a 15mL test tube and add 200 × Centrifuge for 5 minutes. Resuspension the cell particles in MSCM (Qida article number: P2001) complete culture medium and count the total number of cells using a hematocytometer.
5. Use cells for experiments or for passage culture and cryopreservation.
Note: Excessive fusion (over 85%) and prolonged trypsin digestion (over 5 minutes) can have adverse effects on cell viability and quality during cell culture. The cell passage rate should always be between 80% and 85%, while avoiding prolonged incubation in trypsin.







