Technical Support技术支持
CONTACT US
 400 179 0116
400 179 0116
24-hour service hotline marketing@ldraft.comE-mail
marketing@ldraft.comE-mail
Understanding the adipose induction and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
source:QiDa technoligy views:2503 time:2023-09-21
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a type of adult stem cells derived from the early embryonic development mesoderm that possess self-renewal, multi-directional differentiation potential, and can maintain their biological characteristics even after large-scale expansion in vitro. They were first isolated from bone marrow by Friedenstein et al. They have adherent properties and are fibrous in shape. MSCs have rich sources, simple preparation, multi-directional differentiation potential, low immunogenicity, and low tumorigenicity, and are favored by scientific research, Especially in the process of MSC osteogenesis and adipogenic differentiation, it has always been a hot topic in experimental production. Remember to collect the steps for MSC osteogenesis and adipogenic differentiation, and do not get lost during the experiment.
Preparation materials:
1. MSC cells (Qida Biotech can provide MSC cells from humans, rats, mice, New Zealand white rabbits, cows, and pigs, as detailed on the company's website)
2. MSCM medium (Qida Biological: P2001)
3. Osteogenic differentiation medium (Qida Biological, product number: P1301)
4. Adipogenic Culture Medium (Qida Biological, Product No. P1302)
5. 24 hole plate


1、 MSC cell osteogenic/adipogenic differentiation:
In a 24 well plate containing MSCM medium, 50000 to 60000 MSC cells were obtained per well plate.
On the second day or when they reach convergence (usually within 24-48 hours), convert the culture medium into differentiation medium. If the cells are too thin, they will not differentiate, so it is necessary to ensure that MSC cells fuse at least 80% -90% before adding mesenchymal stem cell differentiation medium.
2. Change the fluid every 2-3 days. Note that osteogenic differentiation can easily cause cells to roll up. During osteogenic differentiation, cell culture plates should be coated with coating fluid, and polylysine solution or cell coating fluid (product number: SD0044) can be used for cell coating.
3. Replace fresh mesenchymal stem cell differentiation medium every 1-2 days;
Attention: When changing the fluid, please note that the 24 well plate should be handled gently. The culture medium for changing the fluid needs to be preheated, and the fluid should be slowly dropped along the wall of the well. To prevent osteoblasts from shedding, it is recommended to change the fluid to one and a half times a day after a large amount of calcium nodules appear during the osteogenic process.
4. During the induction period of 14-21 days, staining was performed based on the morphological changes and growth status of the cells.
2、 Cell staining:
1. MSC induced osteogenic differentiation staining:
After inducing osteogenic differentiation, remove the osteogenic differentiation medium from the 6-well plate and rinse 1-2 times with PBS. Add 1 mL of cell fixative to each well and fix for 10 to 30 minutes;
2. Suck off the cell fixative and rinse twice with PBS. Add 1 mL of osteogenic detection dye to each well, incubate at room temperature in darkness for 30 minutes, and check for color development
3. Suck off the staining solution for bone formation testing and rinse with PBS 2-3 times;
4. Place the culture plate under a microscope to observe the osteogenic staining effect;
2. Alizarin red S staining for mineralization detection
Alizarin red S is a calcium sensitive dye. Differentiated osteoblasts deposit a large amount of extracellular calcium (a marker of mineralization), which can be detected by complexing with alizarin red S. The calcium deposition appears as a bright orange red stained area. After taking photos of the alkaline phosphatase stained plate, the plate was washed twice with 1x PBS for alizarin red S staining.
1.adjust the pH value of PBS to 4.2 with 0.1% NH4OH.
2. Extract PBS and add sufficient Alizarin Red S staining solution to cover the cell monolayer. Incubate the tablet in darkness at room temperature for 45 minutes.
3. Carefully absorb the Alizarin Red S solution and clean the board four times with distilled water.
4. Extracellular calcium deposits appear as bright orange red areas.
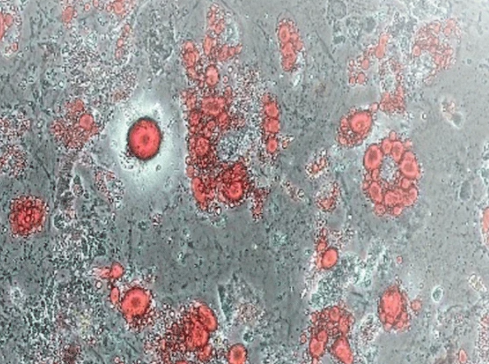
Induction of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells (Day12)
3. Determination of fat differentiation using oil red O staining method
This staining assay is based on the principle of retaining the lipophilic dye oil red O in the visible fat globules of adipocytes under a microscope. The operating steps are as follows:
1. Suck up the culture medium and wash the cells once in PBS.
2. Fix the cells in 4% PFA at room temperature for 15 minutes.
3. Wash twice with ddH2O for 2 x 5 minutes.
4. Stain with Oil-Red-O working solution at room temperature for 15 minutes.
5. Wash with 1x PBS or ddH2O for 3 x 5 minutes.
6. Rinse cells once with 50% isopropanol at room temperature.
7. Rinse cells with 1x PBS or ddH2O.
8. Red stained lipid droplets can be observed through an optical microscope. Adipose cells are also easily observed under a normal microscope through their circular shape and significantly enhanced light reflection of larger lipid droplets.
9. To count the total cells, Mayer HemTox staining agent was used to stain at RT for 15 minutes and washed twice with dd water.
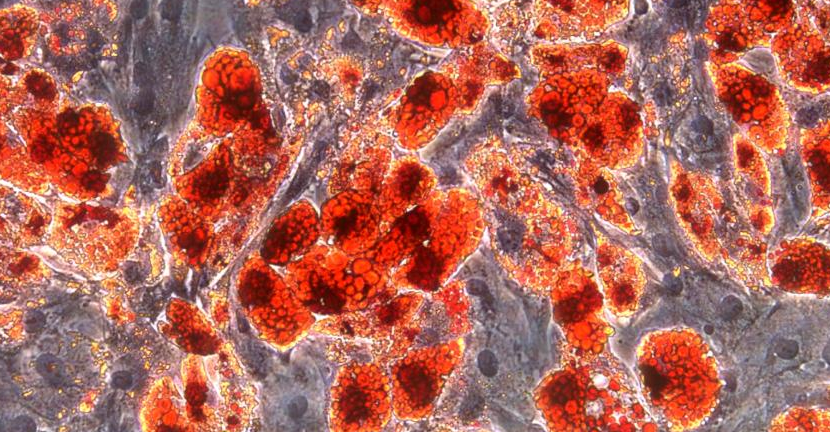
Adipose induction of mesenchymal stem cells (Day10)







