Technical Support技术支持
CONTACT US
 400 179 0116
400 179 0116
24-hour service hotline marketing@ldraft.comE-mail
marketing@ldraft.comE-mail
Do you know these testing methods for angiogenesis?
source:QiDa technoligy views:1809 time:2023-11-09
Angiogenesis, also known as angiogenesis or angiogenesis, refers to the physiological process of producing new blood vessels on the basis of existing ones. Angiogenesis mainly exists in the division and proliferation of endothelial cells. How many detection methods are there for angiogenesis? The following are 31 detection methods found in a literature.

The following are two commonly used experimental detection steps for angiogenesis:
1. MTT method for detecting endothelial cell activity
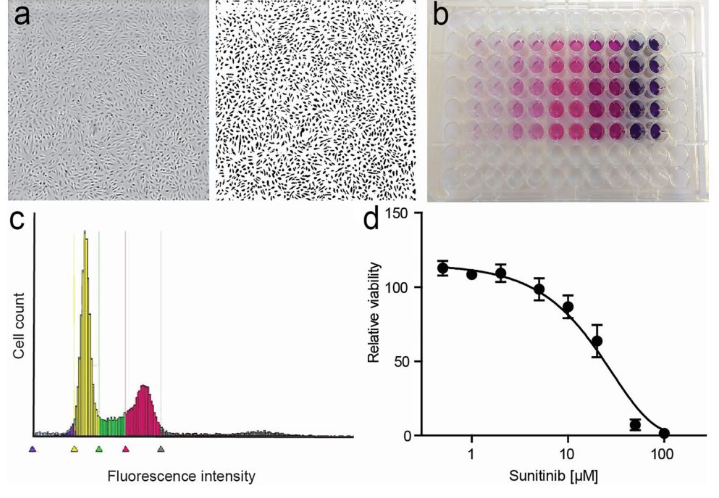
Adherent cell
1. Collect logarithmic phase cells, adjust the concentration of cell suspension, add 100ul per well, lay a plate to adjust the density of the cells to be tested to 1000-10000 wells, (fill the edge wells with sterile PBS).
2. Incubate with 5% CO2 at 37 ℃ until the cell monolayer is covered with the bottom of the well (96 well flat plate), and add a concentration gradient drug. In principle, the drug can be added after the cell adheres to the wall, or for two hours or half a day. However, we often add the drug in the afternoon of the previous day and in the morning of the next day. Generally, 5-7 gradients are set, with each well being 100ul, and 3-5 compound wells are set. It is recommended to set 5 wells, otherwise it is difficult to reflect the real situation.
3. Incubate with 5% CO2 at 37 ℃ for 16-48 hours and observe under an inverted microscope.
4. Add 20ul MTT solution (5mg/ml, i.e. 0.5% MTT) to each well and continue to cultivate for 4 hours. If the drug can react with MTT, centrifuge first and discard the culture medium. Carefully rinse with PBS 2-3 times before adding the culture medium containing MTT.
5. Terminate cultivation and carefully remove the culture medium from the well.
6. Add 150ul of dimethyl sulfoxide to each well and shake at low speed on a shaker for 10 minutes to fully dissolve the crystals. Measure the absorbance values of each well at OD490nm using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. 7. Simultaneously set zero adjustment wells (culture medium, MTT, dimethyl sulfoxide) and control wells (cells, drug dissolution medium of the same concentration, culture medium, MTT, dimethyl sulfoxide).
Suspended cells:
1. Collect logarithmic phase cells and regulate cell suspension concentration 1 × 106/ml, sequentially
① Supplemented 1640 (serum-free) culture medium 40ul;
② Add 10 ul of Actinomycin D (toxic) and dilute l μ g/ml with culture medium. Pre test to find the optimal dilution ratio (1:10-1:20);
③ 10 ul of tested substance;
④ Cell suspension 50ul (i.e. 5 × 104 cells/well), a total of 100ul was added to the 96 well plate (the edge holes were filled with sterile water). Set a control for each board (add 100 μ m (storage solution 100 1640).
2. Incubate at 37 ℃ with 5% CO2 for 16-48 hours and observe under an inverted microscope.
3. Add 10 ul of MTT solution (5 mg/ml, i.e. 0.5% MTT) to each well and continue to culture for 4 hours. (WST-1 is recommended for suspension cells, and step 4 can be skipped after 4 hours of cultivation.) The absorbance values of each well can be measured directly using an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay instrument OD570nm (630nm calibration).
4. Centrifuge (1000 rpm x 10min), carefully remove the supernatant, add 100 ul of dimethyl sulfoxide to each well, and shake at low speed on a shaker for 10 minutes to fully dissolve the crystals. Measure the absorbance values of each well at OD570nm (630nm calibration) using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
5. At the same time, set zero adjustment wells (culture medium, MTT, dimethyl sulfoxide) and control wells (cells, drug dissolution medium of the same concentration, culture medium, MTT, dimethyl sulfoxide), with 3 re wells set for each group.
2、 Steps for the Tubulation Experiment of Endothelial Cells: Taking HUVEC Cells as an Example
Pre cool the consumables required for packaging the substrate adhesive in advance, thaw the substrate film substrate at 4 ° C on ice, wipe and disinfect it with alcohol after thawing, place it on ice for packaging or operation, and shake well before use.
A. Preparation of conditioned medium from target cell lines
1. In order to prepare conditioned medium (CM), target cells were inoculated and grown to 30-40% confluence (depending on the growth rate of the cell line), using serum-free DMEM (e.g. 10ml for T75 tissue culture flask; the presence or absence of antibiotics is irrelevant)
2. Replace the growth medium for 24 hours, and then harvest CM when the cells reach 60-80% convergence in a T75 tissue culture bottle.
If CM is not immediately used after collection, take 0.5 ml of CM aliquot sample and store at -80 ° C.
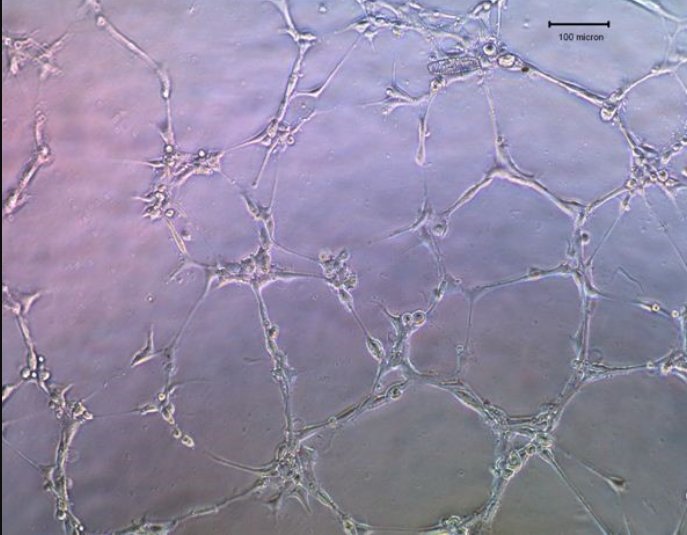
B. Preparation of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC)
1. Prepare ECGM complete culture medium according to the medium ratio requirements.
2. Inoculate HUVEC cells into T25 or T75 culture bottles as needed to achieve 70-80% fusion.
3. Before conducting in vitro formation assays in 200PRF culture medium without antibiotics, remove serum and starve HUVEC cells for 3-6 hours (for example, 5 milliliters for T25 tissue culture bottles).
Note: At the end of serum starvation, proceed to step 1 of procedure C.
4. After coating the 96 well plate with growth factor reduced matrix adhesive, cells were removed from the surface of the flask using trypsin. DMEM was neutralized with serum and centrifuged at room temperature at 1200rpm (276xg) for 3 minutes to precipitate the cells. The cells were resuspended in 2-3ml serum-free DMEM. The concentration of HUVEC was measured by counting the cells, and the cells were aspirated up and down several times to 4 × Resuspension HUVEC cells with 105/ml serum free DMEM to ensure a uniform single cell suspension.
Note: For matrix adhesives with reduced growth factors, the thawing/freezing cycle should be minimized as much as possible.
5. When adding 500 μ Transfer HUVEC cell suspension into a 1.5 ml test tube while thoroughly mixing. Use a desktop centrifuge to slow down the cells for 3 minutes at a speed of 4000rpm (1100rcf). Carefully aspirate the supernatant without interfering with cell sedimentation. Remove as much supernatant as possible. Prepare an appropriate number of HUVEC cells in a 1.5ml test tube based on the number of target cell lines to be used.
Note: Each target cell line CM will suspend one tube of HUVEC, and each suspended HUVEC will be assigned three wells in triplicate. Therefore, a total of 3 wells will be used for each target cell line.
6. Thaw 0.5ml of the target cell line CM collected from step 2 of program A, and supplement it with fetal bovine serum to the final concentration of 1% to resuspend HUVEC cell particles in step 5 of program B.
Note: Each target cell line should be in triplicate (each well requires 100 copies) μ HUVEC cell suspension.
C .Coat 96 well plate with matrix adhesive reduced by growth factor (Qida Bio, product number SD0054)
1. Thaw an appropriate volume of matrix adhesive at 4 ° C the day before use.
2. Pre cool the 96 well plate and pipette tip at -20 ° C for 2-3 hours.
3. At the end of HUVEC cell serum starvation, before counting HUVEC, pre cool each well of the 96 well plate on ice and divide the sample equally by 50 μ L matrix adhesive. Rotate the planking until the gel is evenly distributed over the entire hole. It is very important to avoid the formation of bubbles. Allow it to aggregate on a horizontal surface at room temperature for 1 hour.
D. Distribute HUVEC cells onto the coated 96 well plate
1. Add 100 μ The HUVEC cell suspension obtained in step 6 of program B was completely mixed into the labeled well of the 96 well plate. Incubate the plate at 37 ° C and 5% CO2 for 4-6 hours.
2. Observe cells using an optical microscope. Take an image of the capillary network and use Scion Image software to calculate the length of the pipeline.







